What is High Impedance?
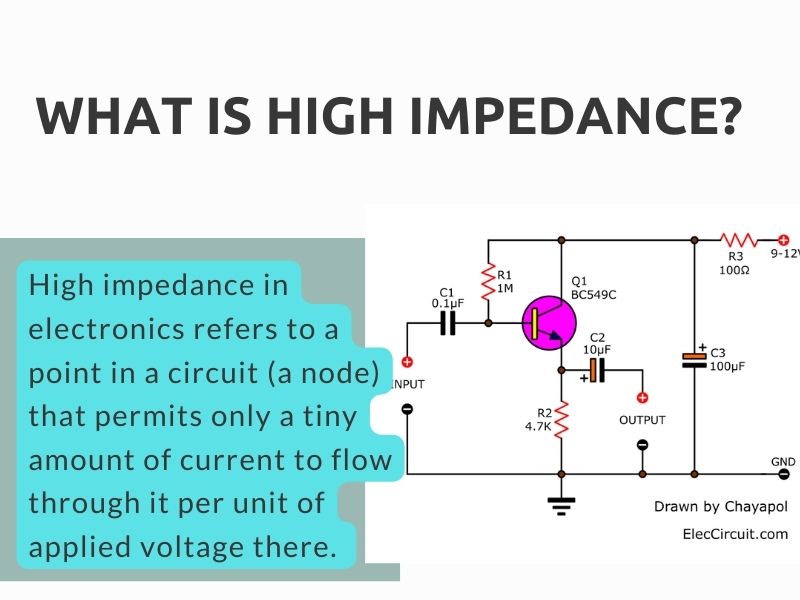
High impedance in electronics refers to a point in a circuit (a node) that permits only a tiny amount of current to flow through it per unit of applied voltage there. Low impedance circuits have high voltage and low current, whereas high impedance circuits are the opposite.
In this article, you will find everything you need to know about high impedance as well as Low impedance in electronics. So stick around until the end to find out what you’ve been looking for.
Where do we use high impedance?
Inputs with high impedance are preferred for measurement devices like oscilloscopes and voltmeters. For usage with equipment like crystal microphones or other items with high internal impedance, an audio system may need a high-impedance input.
Depending on the application, a circuit’s ideal impedance will vary. In audio circuitry, the output impedance of one stage is typically kept low and the input impedance of the stage after that is typically kept high. This is because the value of the voltage is the desired property of the signal that we want to transfer across stages.
In reality, a potential divider is formed by the input impedance of the stage after the preceding one and its output impedance.
Due to the mismatch between the output impedance and the input impedance, any changes in the input impedance of the stage after will not significantly affect the voltage delivered by the stage before, even if they are caused by changes in device characteristics with voltage or frequency, for example.
What happens if the speaker impedance is too high?
An amplifier’s power may not be able to drive the speaker at all if the speaker impedance is too high. When you connect a speaker to an amplifier designed for an 8-ohm impedance but your speaker only has a 4-ohm impedance, this problem arises.
Is it good to have high impedance?
Sources with a high impedance deliver high voltage but little current. For portable power requirements, the equal impedance between the source and the headphones is preferable, but it does not always improve sound quality.
So as explained, it depends on the device and the task you need to be done. It cannot be said whether the high impedance is better or not without using the device or the circuit.
What is low impedance?
Low impedance is defined as being between 4 and 16 ohms. Many sound systems, including home stereo systems and automotive audio systems, use low-impedance speakers. High impedance often refers to an impedance between several hundred and several thousand ohms.
Nightclubs, restaurants, patios, and places of worship, as well as your home or car stereo, frequently have low-impedance sound systems. 25V, 70V, and 100V are used to describe high impedance (often referred to as 70V). For longer cable lengths with multiple speakers on each line, high impedance is desirable.
Is low or high impedance better?
Because it produces higher sound quality, high impedance is preferable. For casual listening on phones or computers, low impedance gear is better suited.
High impedance gear is designed for usage by professionals or audiophiles because it calls for large, specialized gear.
The efficiency with which the electric signal, which is essentially the music, can travel through the speaker is inversely proportional to the impedance. The majority of speakers are rated at 4, 6, or 8 ohms, and less expensive receivers can have trouble driving low-impedance (specifically 4 ohms) speakers.
So you can decide whether to use high impedance or low impedance in your sound systems according to the situation. When you need sounds in an open place low impedance is better while it is a headphone or something similar, then high impedance will be better.
What are low Z and high Z?
The number of wires inside the cable is what really distinguishes high-Z microphone cable types from low-Z microphone cable kinds. Positive and ground are the two conductors used in high-Z cables, while three conductors are used in low-Z cables (positive, neutral, and ground).
When a microphone is a low impedance (low-Z), its output impedance is between 150 and 600 ohms, and when it is high impedance, it is 10,000 ohms or more. (High-Z).
The practical issue is that although high impedance kinds exhibit considerable high-frequency loss with cable lengths larger than roughly 20 feet, low impedance types can be used with cable lengths of 1000 feet or more without a decrease in quality.
Does impedance affect sound quality?
Speaker impedance is only a speaker’s resistance to an amplifier’s current flow. Because the speaker can’t create base-heavy sounds as well, speaker impedance might have an impact on sound quality.
To achieve a suitable balance of audio quality and loudness, the source and headphones are impedance matched. A match does not mean “equal,” it implies “complementary.” It should work well to pair headphones with impedances that are 2.5–8 times greater than the impedance of the source.
How does resistance affect sound quality?
Ohm’s Law states that if the resistance decreases, then the current or voltage must increase, which will need more power than a connected amp can supply.
As a result, your amplifier may eventually sustain major damage and the audio may begin to distort.
Higher impedance headphones (roughly those with a resistance of 25 ohms or more) require more power to produce loud audio levels. They are therefore shielded from harm brought on by overloading. Additionally, a greater variety of audio equipment may be utilized with them.

1/4 Vs 1/2 Watt Resistor: Which One Is Better For Your Project?
RLC talk
Some related FAQs.
Is a keyboard high impedance?
Are higher ohms better?
For example, 100-ohm headphones plugged into a laptop won’t give you the experience you were hoping for because most computers only allow an impedance of 32 ohms.
Are microphones high or low impedance?
The majority of professional microphones have an output impedance of 150 to 250 ohms.
How do I check my microphone impedance?
Polarity is irrelevant since we are measuring resistance, or impedance, hence it makes no difference which probe is attached to which terminal.
Is high sensitivity mic better?
In general, low-sensitivity microphones are preferable for recording loud, isolated sounds. In general, high-sensitivity microphones are preferable for capturing soft, ambient noises.
Watch: Low vs High Impedance Headphones Compared
LCD Displaying Black Boxes Instead Of Text | Arduino Troubleshoot
RLC talk