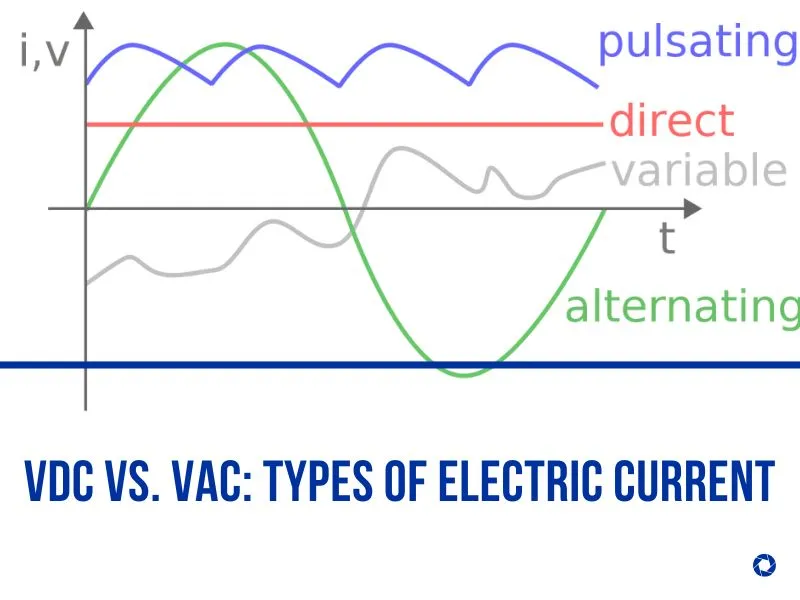
VDC vs. VAC: Types Of Electric Current
Are you aware of the direction in which the Current is flowing? There are two ways electricity moves; Volts Direct Current (VDC) and Volts Alternating Current (VAC). As an electrician, you must know about VDC vs. VAC.
Electricity always flows in a particular direction in a VDC system, similar to how a river runs. As an illustration, consider the flow of electricity produced by batteries, solar cells, etc. VAC is a technique where the positive and negative sides rotate regularly and the flow of current changes as a result.
This is the electricity that comes from a generator or a plug-in. Additionally, alternating current is used to carry electricity produced by power plants and delivered to homes.
In this article, you will know what VDC and VAC are, the difference between VDC and DC, and a complete comparison of VDC vs. VAC. Read on!
What are VDC and VAC?
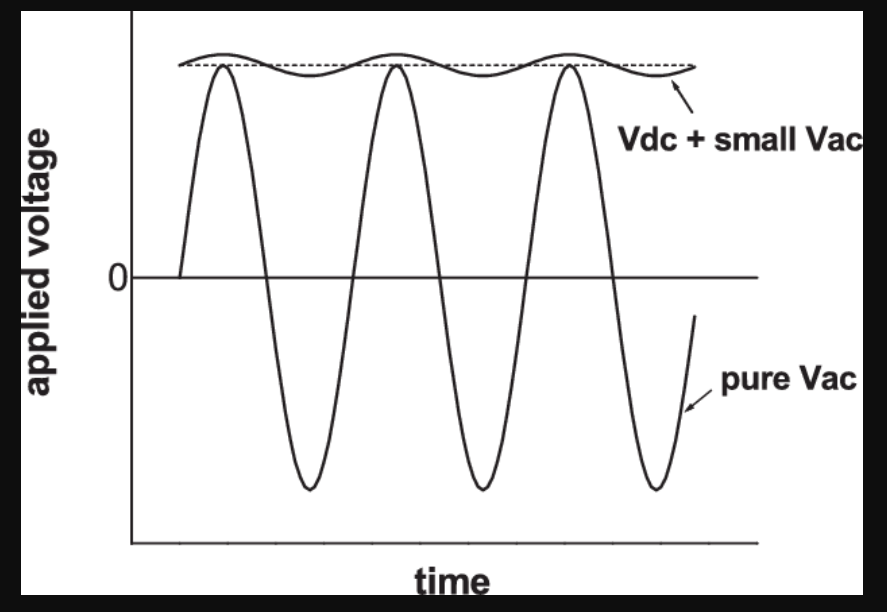
In comparison to VDC vs. VAC, volts of direct Current (VDC), also referred to as volts of direct current, can be produced by a battery or a power source that transforms alternating Current (AC) into direct Current (DC).
The voltage level is constant, and the waves only go in one direction from the wires. DC voltage generation is a relatively easy and straightforward process. A rotating coil produces a voltage in a magnetic field.
The splitter ring and commutator that make up the coil transform alternating electricity into direct voltage. DC’s steadiness is undoubtedly one of its most significant benefits. Much electrical equipment uses DC.
Positive and negative terminals regularly alternate using this technique known as voltage alternating Current (VAC). The current flow changes as a result. Alternating Current is induced in the coil when the conductor that is carrying the current spins in the magnetic field.
The magnetic flux is reduced as the conductor rotates, and the fluctuating flux results in alternating voltage in the conductor. VAC is the voltage applied by a generator or plug-in. Additionally, it serves as an alternating current to distribute electricity produced by power plants to residences.
Is there a Difference between VDC and DC?

The simple answer is yes.
Direct current = DC
Volts Direct Current = VDC
The movement of electrons is referred to as direct Current or DC. Direct current is also known as DC, and VDC stands for volts, Direct Current. VDC is the term for the voltage in a DC circuit. Electrons travel in a DC circuit from the negative terminal to the positive terminal. Here, the path is never altered.
For instance, in the sentence 40 Amp AC/DC, you should understand that the number 40 represents the measurement of Current in AC or DC amperes.
Why Is The Suitable Solder Mask So Essential? Solder Mask Materials.
rlc talk
VDC vs. VAC
- The voltage that generates direct current is referred to as VDC, whereas the voltage that produces alternating current is referred to as VAC.
- While VDC moves in both directions, VAC only moves in one direction.
- The generator produces VAC, and VDC is derived from the battery.
- While the polarity of VAC never changes over time, VDC is always consistent.
- While VDC voltage frequency is zero, VAC frequency varies by nation; primarily, 50 and 60 Hz are utilized.
- While the power factor for VAC might range from 0 to 1, it is always 1 for VDC.
- While VDC does not require phase or neutral, VAC has both.
- While VDC transmission does not require the transformer, VAC transmission must.
- While VDC lacks amplitude, VAC does. The most immense distance traveled by an oscillating or vibrating body is referred to as its amplitude.
- When compared to VDC, VAC has a higher efficiency.
- For VAC, impedance is the neutral characteristic, whereas, for VDC, it is resistance. Impedance is the term for a voltage’s opposition to the current flow.
- Signal amplification is the process of making the signal stronger. The primary benefit of VAC is that it is simple to assess. The ability to readily amplify voltage is a benefit of VDC.
| Comparative Framework | VDC | VAC |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | VDC helps to generate direct current between the two terminals. | VAC helps to generate alternating current between two terminals. |
| Frequency | Zero | Depend on nation |
| Power Factor | Zero | Between 0 – 1 |
| Direction | Stay the same | Vary |
| Generate From | Battery | Generator |
| Efficiency | Low | High |
| Amplitude | Don’t have | Have |
| Advantages | Simple to enhance | Simple to measure |
How To Calculate VDC From VAC?
To determine VDC using VAC, you can use the formula below.
VDC=VAC∗.636
Variables:
From the AC voltage, we may derive VDC, the DC voltage.
VAC means full alternating current voltage.
By multiplying VAC by.636, you may determine VDC using VAC.
Example,
First, determine the total AC voltage.
In this example, the total AC voltage is measured as 120.
Finally, calculate VDC from AC voltage using the formula above:
VDC=VAC∗.636
Adding the above values to the equation results in the following:
VDC= 120∗.636 = 76.32
rlc talk
FAQ.
Are DC and VDC the same?
A DC circuit’s voltage is known as VDC. In a DC circuit, electrons move from the negative to the positive terminal. The road never changes in this place.