MOSFET vs Relay; Best Comparison
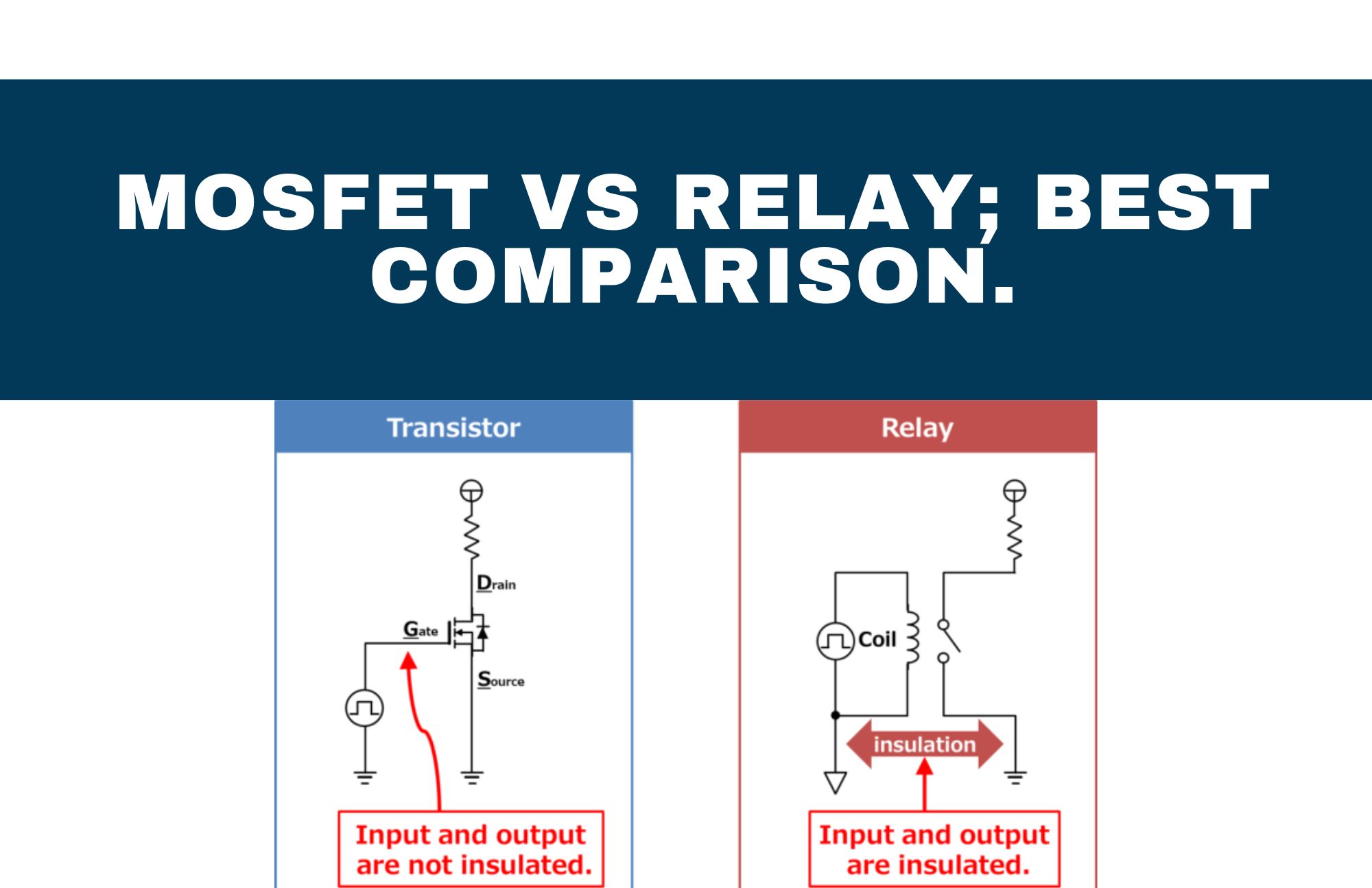
What is the difference between the MOSFET and Relay? Both types of relays are electrically isolated, though a MOSFET is isolated only on the load terminal and an electromechanical relay is isolated on the trigger and load terminals. This could be a crucial defense of an electromechanical relay in safety-related applications.
In this article, you will find everything you need to know when comparing MOSFET with other electronic relays. So I invite you to stick sound until the end to find out what you’ve been looking for and welcome to RLC talk.
Before we start, clarify what those products are, what they are made of, how they work, and their special features of those.
What are MOSFETs?
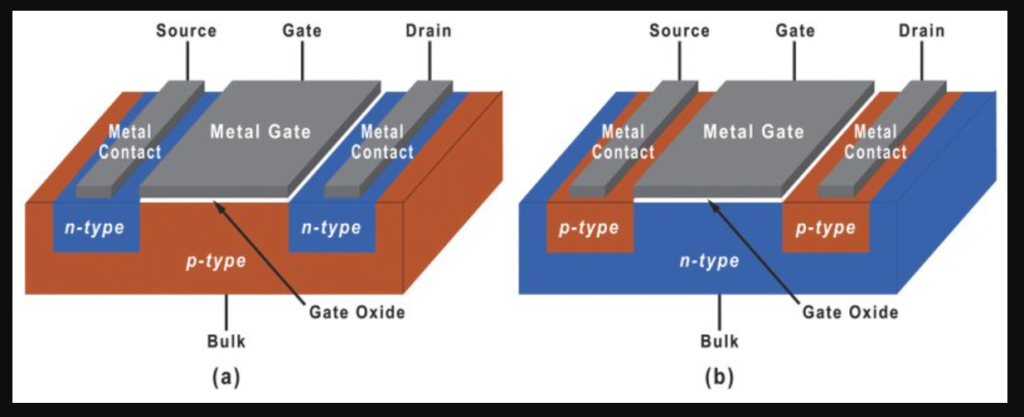
MOSFET stands for “metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistor.” It is a type of transistor that is commonly used in electronic devices such as computers, televisions, and mobile phones.
What are MOSFETs made of?
MOSFETs (Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistors) are made of a semiconductor material, typically silicon, with a thin layer of metal oxide on the surface, which acts as an insulator.
The semiconductor material is usually doped with impurities to create a source and a drain region, and a thin gate electrode is positioned above the oxide layer.
When a voltage is applied to the gate electrode, it creates an electric field that modifies the conductivity of the semiconductor material, allowing the flow of current between the source and the drain to be controlled.
What are MOSFETs used for?
The MOSFET is a type of transistor that uses a metal gate electrode, which is insulated from the semiconductor material by a thin oxide layer.
The source and drain terminals of the MOSFET are made of doped semiconductor material, and the gate terminal is typically made of metal. By applying a voltage to the gate terminal, an electric field is created that modulates the flow of current between the source and drain terminals.
The MOSFET is a voltage-controlled device, which means that the current flowing between the source and drain terminals is determined by the voltage applied to the gate terminal.
This property allows MOSFETs to be used in a wide range of electronic applications, including amplification, switching, and digital logic circuits. They are widely used because of their low power consumption, high input impedance and high input-output isolation.
What are the types of MOSFETs?
There are different types of MOSFETs available, including the
- enhancement-mode MOSFET,
- depletion-mode MOSFET, and
- bipolar junction transistor (BJT) MOSFET.
Each type of MOSFET has its own characteristics and is used in different applications.
What are relays?
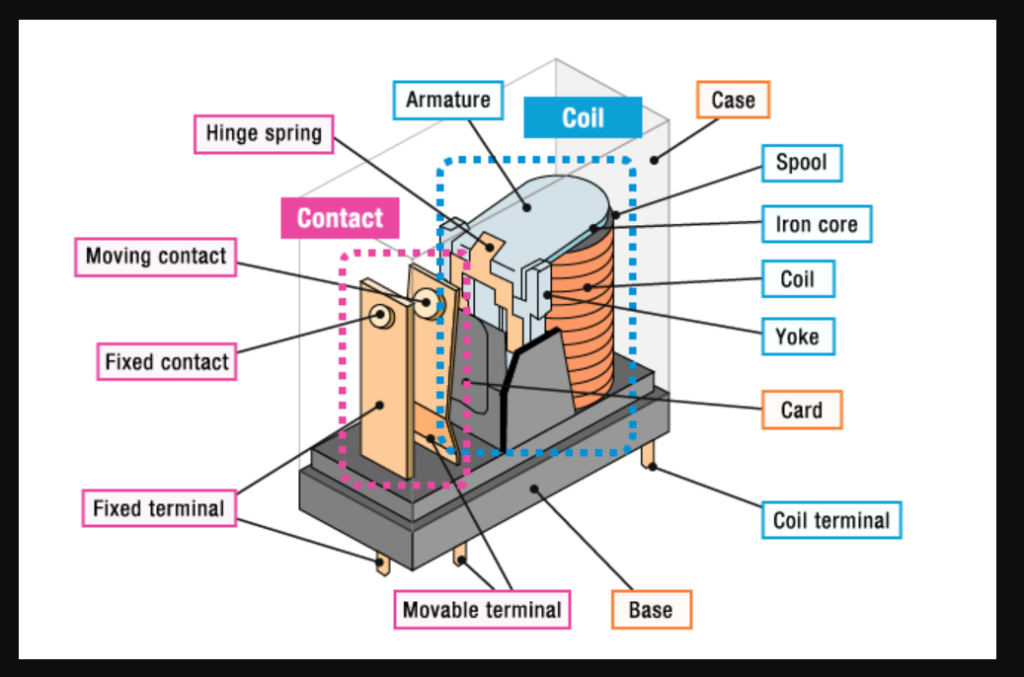
An electrically controlled switch is a relay. It is made up of a set of operating contact terminals and a set of input terminals for one or more control signals. Any number of contacts in different contact configurations, such as make contacts, break contacts, or combinations of both, may be present on the switch.
What are relays made of?
Relays are typically made of metal or plastic and contain an electromagnet and a set of contacts. The electromagnet is activated by an electrical current, which causes the contacts to open or close, allowing or interrupting the flow of electricity through the circuit.
Some relays also contain a coil of wire that generates a magnetic field when electricity flows through it, as well as a spring-loaded armature that moves in response to changes in the magnetic field, which in turn opens or closes the contacts.
What are relays used for?
Relays are used in a wide range of electrical and electronic systems to control the flow of electricity. They are used to switch circuits on and off, control the direction of current flow, and to provide electrical isolation between different parts of a circuit.
Automotive systems: Relays are used in cars to control the headlights, turn signals, and other electrical systems.
Industrial control systems: Relays are used in factories and other industrial settings to control motors, lights, and other equipment.
Telecommunications systems: Relays are used in telephone and data networks to route calls and transmit information.
Home appliances: Relays are used in many household appliances, such as washing machines, refrigerators, and air conditioners, to control the flow of electricity to different components.
Computers and electronic devices: Relays are used in computers and other electronic devices to control the power supply and to provide protection against overcurrent and overvoltage.
Safety applications; Where human safety is at risk, like in Fire-alarm systems, emergency shut off, gas leakage detection, and more.
What are the types of relays?
There are several different types of relays, each with its own unique characteristics and uses. Some common types of relays include:
Electro-mechanical relays:
These relays use an electromagnet to open and close a set of contacts. They are widely used in industrial and commercial applications and can handle relatively high currents and voltages.
Solid-state relays:
These relays use semiconductor devices, such as transistors, to open and close a circuit. They have no moving parts and are more reliable and durable than electro-mechanical relays, but typically handle lower currents and voltages.
Reed relays:
These relays use a reed switch, which is a type of switch that is activated by a magnetic field. They are small, fast, and have low power consumption, but are not suitable for use with high currents or voltages.
Mercury wetted relays:
As the name suggests this type of relay uses mercury in its contacts, and it is activated by a magnetic field. these relays are used in high-current applications and when high-precision switching is needed.
The Rainbow of Solder Mask Colors: Which is Right for Your PCB?
Rlc talk
What do MOSFETs and Relays have in common?
MOSFETs (Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor) and relays are both electronic devices that are used to control the flow of electricity in a circuit.
Some of the similarities between MOSFETs and relays include:
- Both are used to switch electrical circuits on and off, or to control the direction of current flow.
- Both can be used to provide electrical isolation between different parts of a circuit.
- Both can be controlled using an electrical signal, such as a voltage or a current.
- Both can be used in a wide range of applications, including industrial control systems, automotive systems, telecommunications systems, and home appliances.
- Both can handle high power and operate in high voltages, but relays are generally better suited for high current applications than MOSFETs.
MOSFET vs Relay: What are the differences?
| Feature | MOSFET | Relay |
|---|---|---|
| Switching Mechanism | Semiconductor | Mechanical |
| Switching Speed | High | Low |
| Lifetime | High | Moderate |
| Power Handling | Medium to High | High |
| Current Handling | Medium | High |
| Voltage Handling | High | High |
| Size | Small | Large |
| Noise Level | Low | Moderate |
| Immunity to environmental factors | High | Low |
| Cost | Moderate to High | Low |
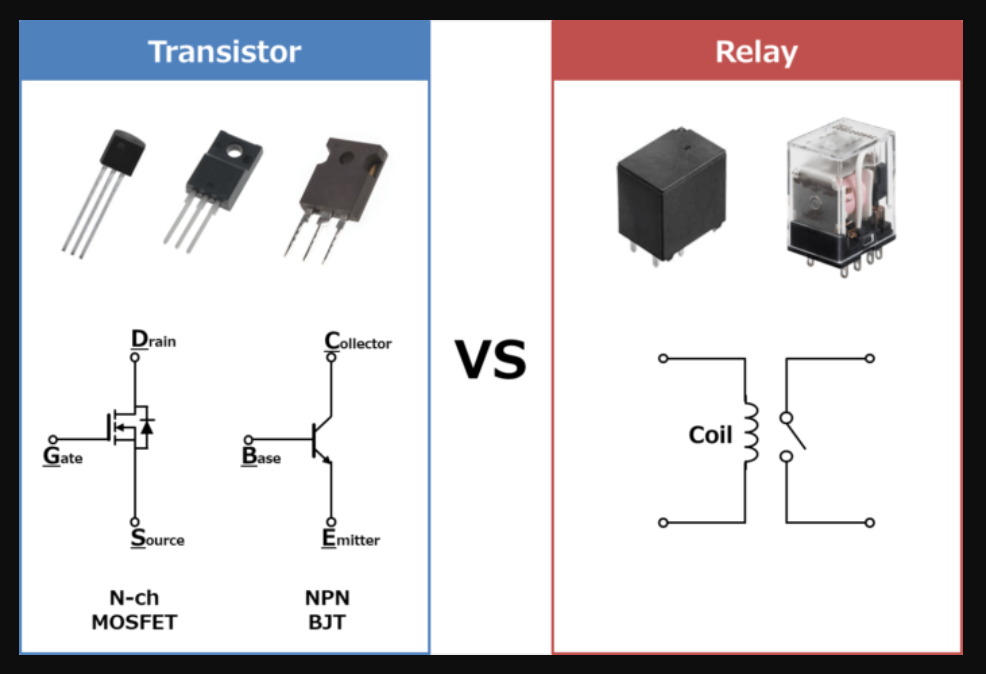
It’s important to note that MOSFETs and relays both have their own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice between them depends on the specific requirements of the application.
Generally speaking, MOSFETs are more suitable for applications that require fast switching speed, high frequency operation, or low noise level, while relays are better suited for high-current applications or where mechanical switch contacts are needed.
Are MOSFETs better than relays?
In many applications, a MOSFET relay performs better than an electromechanical relay. It is a solid-state device that drives a MOSFET from an optically isolated input stage in place of a mechanical switch that is activated by a coil.
MOSFETs and relays have their own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice between them depends on the specific requirements of the application.
In general, MOSFETs tend to be more suitable for applications that require fast switching speed, high frequency operation, or low noise level. They are also more reliable and durable than relays.
On the other hand, relays are better suited for high-current applications or where mechanical switch contacts are needed.
Do I need Flux with Rosin Core Solder?
RLC talk