How to Rotate in LTspice?
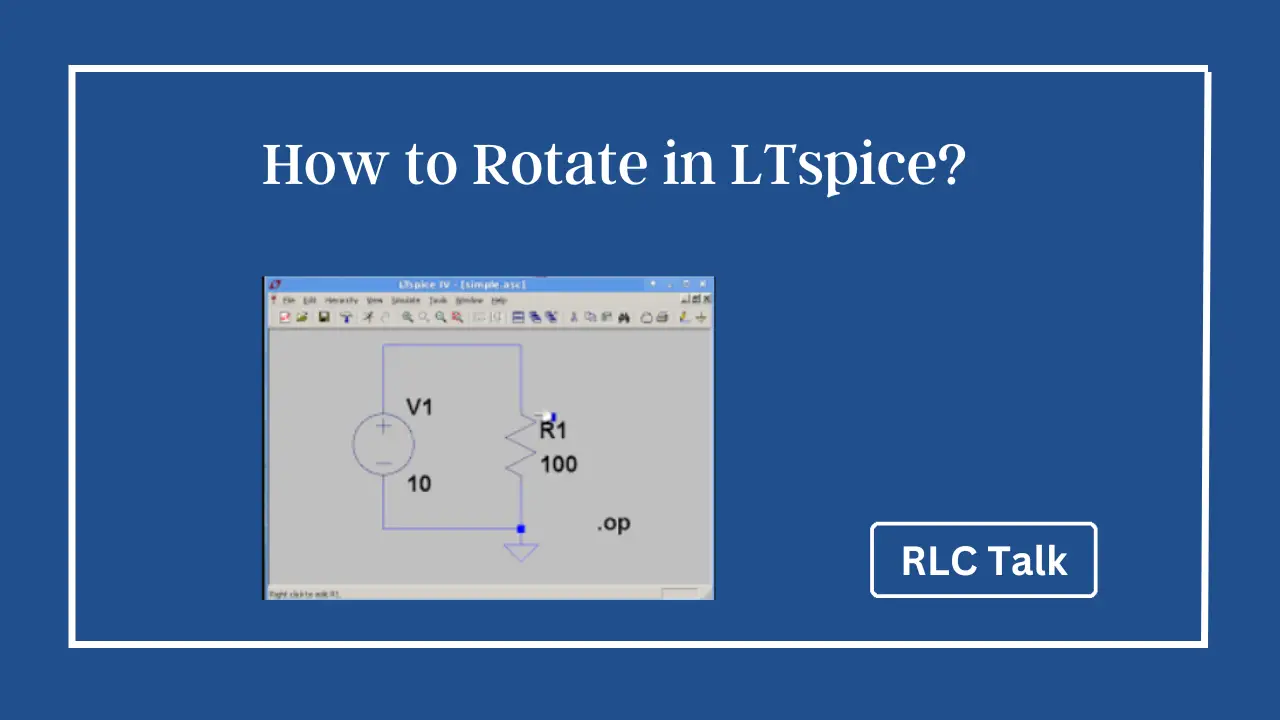
Rotating components in LTspice is straightforward. In the graphical interface, select the component and use the rotate handle to change its orientation. Alternatively, use the rotate command in the schematic editor for precise rotation angles. Rotation improves circuit visualization, helps analyze behavior, and ensures optimal circuit layout. Experiment with rotation to enhance your LTspice simulations.
LTspice has become a popular choice among engineers and hobbyists in simulating electronic circuits. With its powerful capabilities and user-friendly interface, LTspice allows for in-depth analysis of circuit behavior.
One useful feature in LTspice is the ability to rotate components and circuit elements. In this article, we will explore the concept of rotation in LTspice, its practical applications, and provide tips for effective utilization.
What is rotation in LTspice?
In LTspice, rotation refers to the act of changing the orientation of components, voltage sources, current sources, and other circuit elements within a schematic.
It serves multiple purposes, such as optimizing visual clarity, analyzing circuit behaviour under different orientations, and simulating complex circuit layouts.
What are the rotating Components in LTspice?
In LTspice, you can easily rotate various components to suit your circuit design needs. This includes rotating resistors, capacitors, inductors, transistors, diodes, and even integrated circuits (ICs).
By rotating these elements, you can better align them with the desired circuit configuration or improve the readability of your schematic.
Rotating Voltage and Current Sources
Voltage and current sources play a crucial role in circuit simulations. In LTspice, you have the flexibility to rotate both DC and AC voltage sources and current sources.
This allows you to align them with the circuit layout for better visualization and analysis. Additionally, behavioral voltage and current sources can also be rotated to match your circuit requirements accurately.
What are the practical applications of Rotation in LTspice?
Rotating components and circuit elements in LTspice offers practical benefits in circuit simulations. Firstly, rotating components can enhance the visual clarity of the schematic, making it easier to understand and analyze complex circuits.
Secondly, by examining circuit behavior under different orientations, you can gain insights into the impact of component placement on performance. Lastly, rotation enables the simulation of intricate circuit layouts and wiring configurations, facilitating accurate representation of real-world scenarios.
How many transistors does a NAND gate have?
rlctalk.com
Tips and Best Practices for Rotating in LTspice
To make the most out of rotation in LTspice, it is essential to familiarize yourself with the available tools and shortcuts. You can easily rotate components and sources using the graphical interface by selecting the desired element and the rotate handle.
Alternatively, the schematic editor provides a rotate command for precise rotation angles. Learning keyboard shortcuts and employing time-saving techniques can significantly improve your productivity while rotating elements in LTspice.
How to mirror components in LTspice?
Mirroring components in LTspice can be done using the “Mirror” feature in the graphical interface. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to mirror a component in LTspice:
- Open LTspice and create or open a schematic to mirror a component.
- Select the component you wish to mirror by clicking on it.
- Right-click on the selected component to open the context menu.
- In the context menu, navigate to the “Mirror” option and click on it.
- The selected component will be mirrored, reflecting its image along the vertical axis.
- Adjust the mirrored component’s position to align it properly within the circuit.
By mirroring components, you can create symmetrical layouts, analyze circuit behavior in different orientations, or match specific circuit requirements. Experimenting with mirrored components can help optimize circuit design and enhance understanding of circuit performance.
Remember to save your schematic after mirroring the component to preserve the changes for future simulations or further modifications.
Please note that not all components can be mirrored, particularly those with asymmetrical or non-reversible properties. However, most basic passive components like resistors, capacitors, and inductors can be mirrored without issues.
By utilizing the mirroring feature in LTspice, you can further refine your circuit layout and explore different configurations to achieve your desired circuit design goals.
Learn How To Make Money From Solder Repair For More Income In 2023
rlctalk.com
Conclusion
Rotation is a valuable feature in LTspice that empowers users to manipulate the orientation of components, voltage sources, and current sources within circuit simulations.
By understanding and effectively utilizing rotation, you can optimize visual clarity, analyze circuit behaviour, and simulate complex circuit layouts. Embrace the power of rotation in LTspice to enhance your circuit visualization and analysis capabilities, ultimately improving circuit designs and insights.