Maximizing Alternator Lifespan: A Comprehensive Guide to Exciting Your Alternator
Are you having trouble getting your alternator to generate electricity? Do you want to learn how to excite your alternator properly to ensure maximum performance? Then keep reading!
Alternators are crucial components in any electrical system, but they can’t function without being properly excited. Excitation is the process of providing an initial electric current to start the electrical generation process. In this article, we will discuss everything you need to know about how to excite an alternator.
By learning how to properly excite your alternator, you can ensure that your electrical system is functioning efficiently and effectively. You’ll be able to identify and troubleshoot common issues that arise during excitation, and take the necessary steps to resolve them quickly.
Let’s get started by discussing the basics of alternator excitation, the steps involved in exciting an alternator, and common issues you may encounter during the process.
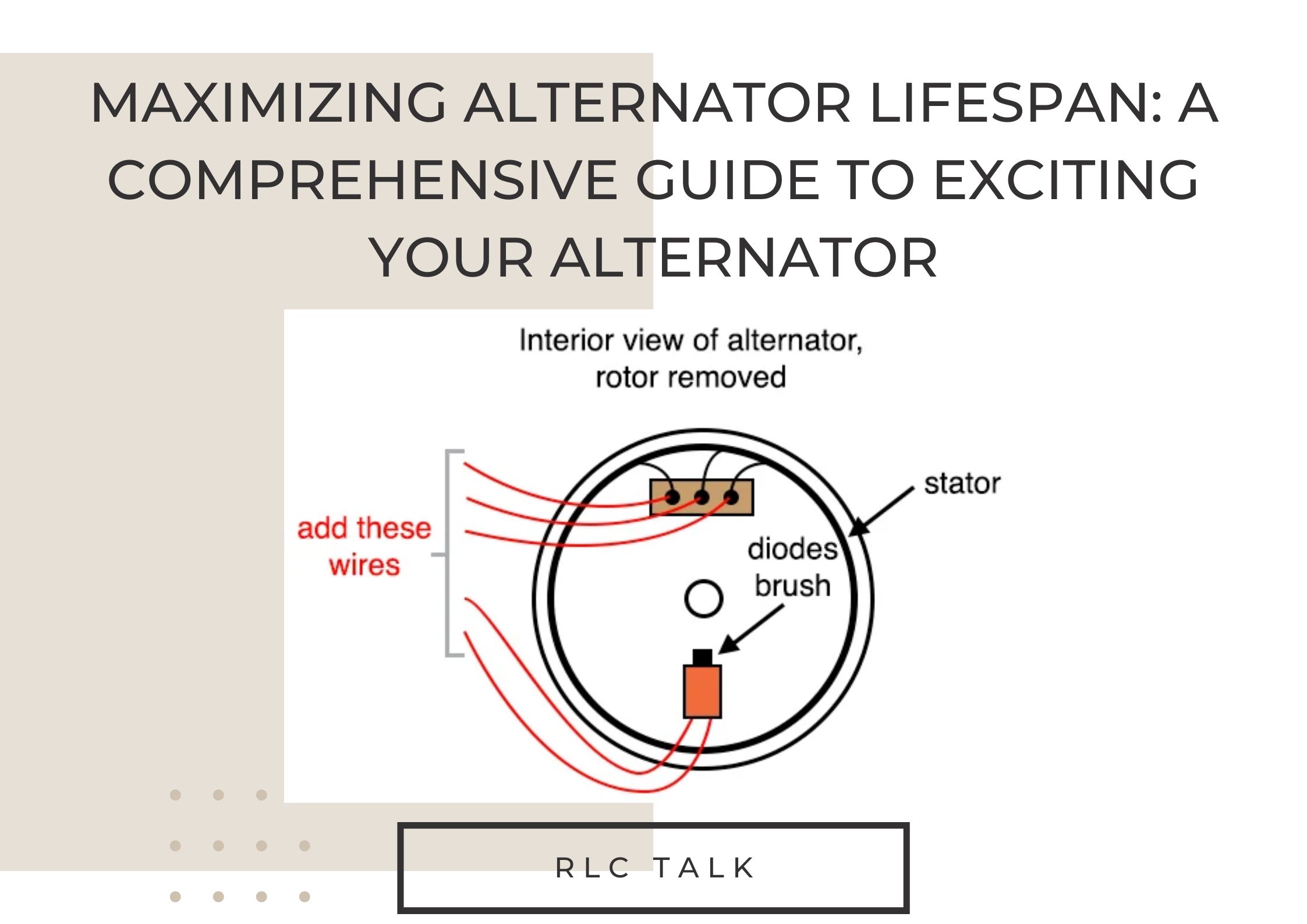
Excitation is the process of providing an initial electric current to start the electrical generation process in an alternator. This current creates a magnetic field that induces a current flow in the stator windings. Without this initial current, the alternator will not generate any electricity.
There are two types of excitation: self-excitation and external excitation. Self-excitation is when the alternator uses a residual magnetic field from a previous operation to create a voltage that starts the electrical generation process. External excitation is when an external source is used to provide the initial current flow to start the electrical generation process.
Factors That Affect Alternator Lifespan
A faulty battery can significantly reduce the lifespan of an alternator. The battery acts as a power source for the alternator to generate electricity. If the battery is weak or dead, the alternator has to work harder to keep the electrical system running, putting more strain on the alternator. The alternator has to produce more power to compensate for the battery, which can lead to increased wear and tear on its components. Over time, this can cause the alternator to fail prematurely.
The quality of the alternator is another factor that affects its lifespan. Cheaper, lower-quality alternators may not be built to last and may fail sooner than their higher-quality counterparts. Quality alternators are made with high-grade materials and are designed to withstand the demands of the electrical system.
They have better internal components that are less likely to wear out or break down over time. Cheaper alternators may seem like a cost-effective solution initially, but they can end up costing more in the long run due to the need for frequent replacements and repairs.
Harsh driving conditions can also decrease the lifespan of an alternator. Extreme temperatures, high humidity, and dusty environments can cause damage to the alternator’s internal components, causing them to wear out faster. In extreme heat, the alternator’s cooling system may not be able to keep up, leading to overheating and potential damage to the alternator.
In dusty environments, the alternator’s air intake may become clogged with debris, reducing its efficiency and causing it to work harder to generate electricity.
Steps to Excite an Alternator
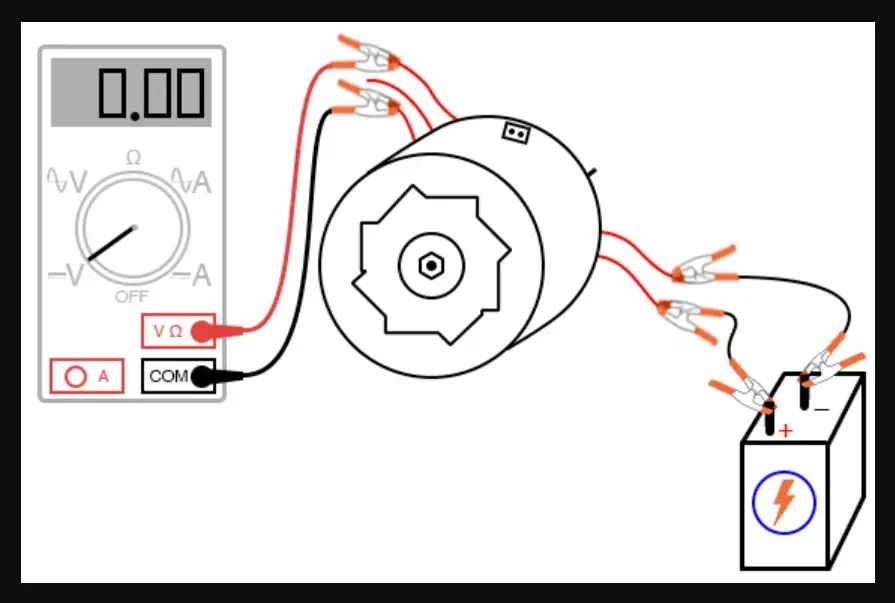
Exciting an alternator is a process that allows the alternator to begin generating electricity. The process is essential for the proper functioning of the electrical system in your vehicle. If your alternator is not properly excited, your vehicle’s battery may not charge, and your electrical system may not operate correctly. Here are the steps to excite an alternator properly.
Start the Engine
The first step to excite an alternator is to start the engine. Once the engine is running, the alternator can begin generating electricity. The alternator is driven by the engine through a belt, and it begins to spin as soon as the engine is running.
Connect the Battery
The next step is to connect the battery to the alternator. The battery provides the initial power to excite the alternator. The positive and negative terminals on the battery should be connected to the corresponding terminals on the alternator. This will complete the circuit and allow the alternator to begin generating electricity.
Rev the Engine
Once the battery is connected, you need to rev the engine to a certain RPM to excite the alternator. The exact RPM required may vary depending on the make and model of your vehicle, so it’s important to consult your owner’s manual for the specific instructions. In most cases, revving the engine to around 2000 RPM should be sufficient to excite the alternator.
Check the Voltage
After revving the engine, you should check the voltage output of the alternator to ensure that it is generating electricity properly. You can use a voltmeter to check the voltage. The voltmeter should be connected to the battery terminals to measure the voltage output. The voltage output should be around 14 volts or higher, indicating that the alternator is generating electricity properly.
Turn Off Electrical Load
Once you’ve confirmed that the alternator is generating electricity properly, you should turn off any electrical loads in the vehicle. This will reduce the electrical load on the alternator, allowing it to operate more efficiently.
If you don’t turn off electrical loads, such as the headlights or air conditioning, the alternator may have to work harder to keep up with the demand, leading to increased wear and tear on its components.
Monitor the Voltage
Finally, you should monitor the voltage output of the alternator to ensure that it remains within the proper range. The voltage output should be around 14 volts or higher when the engine is running and no electrical loads are on. If the voltage output drops below 13 volts, it may indicate a problem with the alternator or the electrical system in your vehicle.
DIY Cable Management: The Easy Way to Hide Ethernet Cables Along Walls
rlc talk
How to Extend Alternator Lifespan
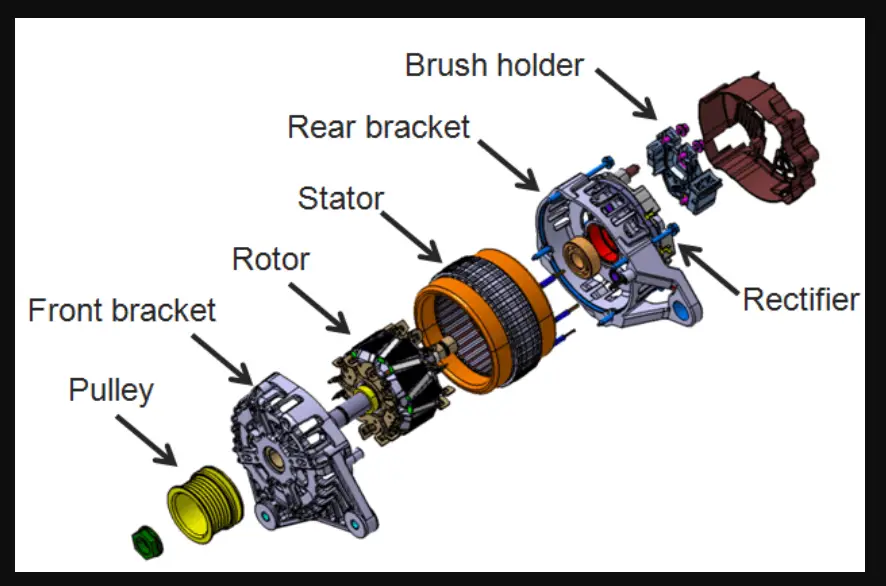
There are several things you can do to extend your alternator’s lifespan. Firstly, make sure you’re using a high-quality battery that’s in good condition. A weak or dead battery can put more strain on the alternator, leading to premature failure. Secondly, avoid harsh driving conditions whenever possible. Extreme temperatures, high humidity, and dusty environments can all take a toll on your alternator.
Regular maintenance is also essential for extending your alternator’s lifespan. Have your alternator checked regularly by a qualified mechanic to ensure it’s in good condition. Additionally, make sure the alternator belt is tight and in good condition, as a loose or worn belt can cause the alternator to work harder than it needs to, leading to premature failure.
Tips for Exciting Your Alternator
One of the most important things you can do to maximize your alternator’s lifespan is to keep it properly excited. Exciting your alternator simply means providing it with the correct amount of voltage to produce electricity. Alternators require a certain amount of voltage to produce electricity, and if that voltage isn’t supplied, the alternator won’t work correctly.
To excite your alternator, start your car and let it run for a few minutes. Then, turn on all of your car’s electrical components, including the headlights, radio, and air conditioning. This will provide the alternator with the correct amount of voltage to produce electricity. If you notice any issues with your car’s electrical system, such as dimming headlights or a warning light on the dashboard, it’s important to have your alternator checked by a qualified mechanic.
How Often Should an Alternator Be Replaced?
There’s no set lifespan for an alternator, as it can vary depending on several factors, as we’ve discussed. However, most alternators will last between 80,000 and 150,000 miles, depending on driving conditions and other factors.
It’s important to have your alternator checked regularly by a qualified mechanic to ensure it’s in good condition. If your alternator does need to be replaced, it’s essential to have it replaced as soon as possible to avoid any further damage to your car’s electrical system.
Common Alternator Problems and Their Solutions
There are several common issues that can arise with an alternator. One of the most common is a loose or worn alternator belt. If the alternator belt isn’t tight or is worn, it can cause the alternator to work harder than it needs to, leading to premature failure. The solution is to have the belt tightened or replaced as needed.
Another common issue is a faulty voltage regulator. The voltage regulator is responsible for regulating the voltage produced by the alternator. If the voltage regulator is faulty, it can cause the alternator to overcharge or undercharge the battery, leading to premature failure. The solution is to have the voltage regulator replaced by a qualified mechanic.
Your alternator is a critical component of your car’s electrical system. To maximize its lifespan, make sure you’re using a high-quality battery, avoid harsh driving conditions, and keep your alternator properly excited. Regular maintenance is also essential, including having your alternator checked by a qualified mechanic regularly. By following these tips, you can help ensure your alternator lasts as long as possible, keeping your car running smoothly and reliably.
How many transistors does a NAND gate have?
rlc talk