Zinc Phosphate 101: Cracking the Code of Its Chemical Formula
Zinc Phosphate is a white crystalline compound that may not seem like much at first glance, but it has remarkable properties that make it stand out. It has excellent corrosion resistance, adhesion properties, and strength, making it an essential material in paint, coating, metallurgy, and dentistry industries.
Zinc Phosphate is not only a highly effective coating material for metal surfaces, but it also acts as a fluxing agent to remove impurities during welding, soldering, and brazing. It is biocompatible and strong enough to be used as a cementing agent for dental restorations and bone substitutes. Additionally, its unique chemical formula makes it an interesting compound to study for those interested in inorganic chemistry.
Who wouldn’t want a material that can protect metal surfaces from corrosion, remove impurities during welding, and provide strong and biocompatible dental restorations? Zinc Phosphate can be a game-changer for many industries, leading to better performance, longevity, and cost savings.
What is Zinc Phosphate?

Zinc Phosphate is an inorganic chemical compound that consists of zinc cations and phosphate anions. It is a white crystalline powder that is soluble in acids and insoluble in water. Zinc Phosphate is widely used in various industries due to its unique properties.
One of the main applications of Zinc Phosphate is as a coating material for metal surfaces. When applied to metal surfaces, Zinc Phosphate forms a protective layer that prevents corrosion and rusting. This is because Zinc Phosphate reacts with the metal surface to form a thin layer of Zinc Orthophosphate, which acts as a barrier to prevent further oxidation.
Zinc Phosphate is also used as a fluxing agent during welding, soldering, and brazing. Fluxes are materials that are used to remove impurities and oxides from metal surfaces to ensure proper bonding. Zinc Phosphate is an excellent fluxing agent because it is reactive with both the metal surface and the impurities, forming a low-melting-point glassy phase that dissolves the impurities and promotes bonding.
Another important application of Zinc Phosphate is in dentistry. It is used as a cementing agent for dental restorations, such as crowns, bridges, and implants. Zinc Phosphate cement is biocompatible, meaning it is not harmful to living tissues and provides a strong bond with the tooth structure. The cement sets quickly and has a high compressive strength, making it an ideal material for dental restorations.
Zinc Phosphate is also an interesting compound to study for those interested in inorganic chemistry. It has a unique crystal structure that can be studied using X-ray crystallography, and its properties can be modified by doping with other elements, such as magnesium or calcium.
Counting 10 THHN in 3-4 EMT: A Quick and Easy Guide
rlc talk
What is the Chemical Formula of Zinc Phosphate by Steps?
The chemical formula of Zinc Phosphate can be determined by understanding the valence electrons and charges of the zinc cation and phosphate anion. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of the process:
Step 1: Determine the valence electrons of the elements in the compound.
Zinc (Zn) has a valence of +2, meaning it has two valence electrons that can be donated to form a bond. Phosphate (PO4) has a valence of -3, meaning it has three electrons available for bonding.
Step 2: Determine the charges of the ions in the compound.
Zinc has a charge of +2 because it has two electrons available to donate, while Phosphate has a charge of -3 because it has three electrons to accept.
Step 3: Use the charges to balance the formula.
We need two phosphate anions to bond with one zinc cation to balance the charges. This gives us the chemical formula Zn3(PO4)2.
It’s important to note that Zinc Phosphate can exist in different forms depending on the number of water molecules present in the compound. For example, Zinc Phosphate can form a dihydrate compound with two water molecules, which would be represented as Zn3(PO4)2.2H2O.
Zinc Phosphate can also form a trihydrate compound with three water molecules, represented as Zn3(PO4)2.3H2O. These hydrates can have different physical and chemical properties than anhydrous Zinc Phosphate, making them useful in various applications.
In the paint and coating industry, for example, the trihydrate form of Zinc Phosphate is used as a pigment to provide excellent adhesion and corrosion resistance. In dentistry, the dihydrate form of Zinc Phosphate is used as a cementing agent for dental restorations.
Examples of Zinc Phosphate
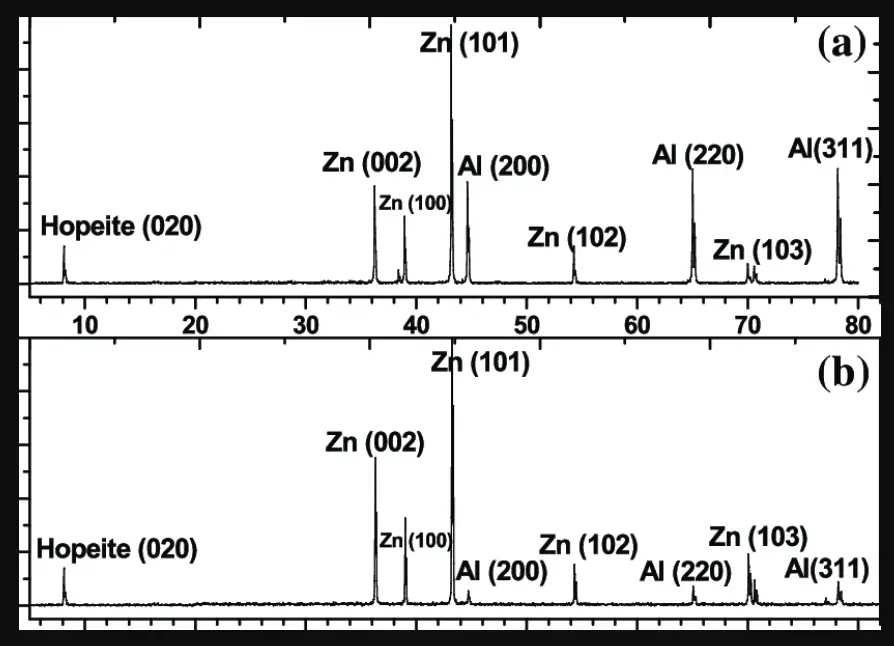
Zinc Phosphate is a versatile compound that finds its use in various applications across different industries. Here are some examples of Zinc Phosphate and their applications:
Paints and Coatings
Zinc Phosphate is widely used in the paint and coating industry as a corrosion inhibitor and pigment. Its ability to provide excellent adhesion and corrosion resistance has made it a preferred choice in the production of primer coatings.
The Zinc Phosphate pigment is also used in the formulation of high-performance paints for military vehicles, offshore structures, and industrial equipment.
Dental Cement
Zinc Phosphate is used as a dental cementing agent in restorative dentistry. The compound is mixed with water to form a paste that is applied to the teeth before the restoration process. Once the paste hardens, it forms a strong bond with the tooth structure, providing excellent retention for dental restorations such as crowns, bridges, and inlays.
Fertilizers
Zinc Phosphate is used in the production of fertilizers to provide essential nutrients to plants. The compound is an excellent source of zinc and phosphorus, essential micronutrients required for plant growth and development.
Zinc Phosphate fertilizers are effective in treating zinc and phosphorus deficiencies in plants, improving their yield and quality.
Corrosion Protection
Zinc Phosphate is used as a corrosion inhibitor in the production of metal coatings and primers. The compound provides a protective layer on metal surfaces, preventing rust and corrosion from occurring. Zinc Phosphate is commonly used in the automotive and aerospace industries, where metal parts are exposed to harsh environmental conditions.
Pharmaceutical Industry
Zinc Phosphate is used in the pharmaceutical industry as a source of zinc for supplements and medications. Zinc is an essential mineral that is vital to the immune system, wound healing, and protein synthesis. Zinc Phosphate supplements are used to treat zinc deficiency, which can lead to various health problems such as growth retardation, impaired immune function, and skin disorders.
In conclusion, Zinc Phosphate is a versatile compound that finds its use in various applications across different industries. Its ability to provide excellent adhesion, corrosion resistance, and essential micronutrients makes it a preferred choice in the production of paints, dental cements, fertilizers, and corrosion protection coatings.
Understanding the chemistry and different applications of Zinc Phosphate can help us appreciate its importance in our daily lives. With ongoing research and development, Zinc Phosphate is likely to continue playing a critical role in various industries for years to come.
Understanding How Various Battery Types Are Affected By Magnetic Fields
rlc talk